

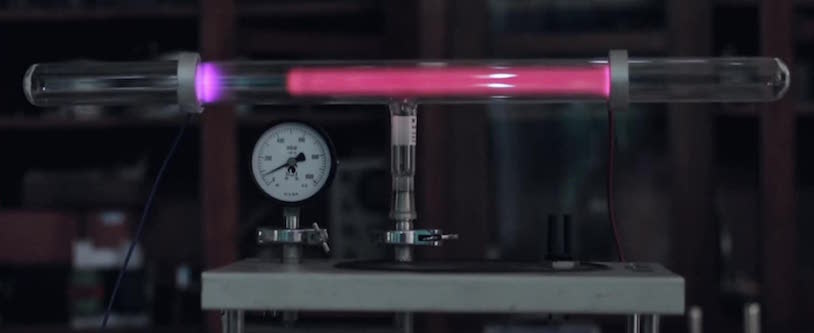
In 1857 the German glassblower Heinrich Geissler, while working for fellow countryman and physicist Julius Plücker at the University of Bonn, improved the quality of the vacuum that could be achieved in such tubes. image ©įaraday is famous for discovering and naming the electron.Īdvancing technology moves science forward Like what Faraday saw, the tube shows a dark space between the glows around the cathode (left, negatively charged) and anode (right, positively charged). Figure 1: Glow discharge in a low-pressure tube caused by electric current. Faraday couldn’t fully explain his observations, and it took a number of further developments in terms of the technology of the tubes, before a greater understanding emerged. This left an area between the cathode and the start of the luminescence that was not illuminated, and subsequently became known as Faraday’s dark space (Figure 1). In his experiments, Faraday observed a luminescence that started part way down the tube, and traveled toward the anode. The arc started at the negative plate (known as the cathode) and traveled through the tube to the oppositely charged anode (Faraday, 1838). In 1838, Faraday noted that when passing a current through such a tube, an arc of electricity was observed. Rarefied air referred to a system in which most of the gaseous atoms had been removed, but where the vacuum was not complete. However, one of Faraday’s earliest experimental observations was a crucial precursor to the discovery of the first subatomic particle, the electron.Īs early as the mid-17th century, scientists had been experimenting with glass tubes filled with what was known then as rarefied air. Somewhat paradoxically, all of Faraday’s pioneering work was carried out prior to the discovery of the fundamental particle that these electrical phenomena depend upon. The English scientist Michael Faraday can reasonably be considered one of the greatest minds ever in the fields of electrochemistry and electromagnetism. Several scientists working on atomic models found that atoms were not the smallest possible particles that made up matter, and that different parts of the atom had very distinct characteristics. For the previous version, please go here.īy the late 1800’s, John Dalton’s view of atoms as the smallest particles that made up all matter had held sway for about 100 years, but that idea was about to be challenged.

This is an updated version of our Atomic Theory I module.
The Case of the Ivory-billed Woodpecker.Santiago Ramón y Cajal and Camillo Golgi.Factors that Control Earth's Temperature.Plates, Plate Boundaries, and Driving Forces.Solutions, Solubility, and Colligative Properties.Y-Chromsome and Mitochondrial DNA Haplotypes.Absorption, Distribution, and Storage of Chemicals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
